The Intelligence Quotient scores are the measure of cognitive ability compared with the same-age peers of others. IQ scores can give insight into problem-solving abilities, reasoning, and overall intellectual performance. However, a lot of people ask how the IQ score changes with age and what really the numbers on the scale mean. Read on for a detailed explanation of IQ scores and their interpretation at each stage of life.
What is an IQ Score?
An IQ score is a standardized measure of intelligence, derived from a series of tests designed to assess logical reasoning, problem-solving abilities, memory, and comprehension. The average IQ score is set at 100, with the majority of the population scoring between 85 and 115.
The Importance of Age in IQ Testing
IQ scores are calculated based on age because cognitive abilities typically develop with age, especially in children. By comparing a person’s score to others in their age group, IQ tests aim to provide a relative measure of intellectual ability. This means an IQ score of 100 indicates average intelligence for a particular age group.
Understanding the IQ Score Chart by Age
1. IQ Scores for Children (0-12 years)
- Ages 2-4: IQ tests administered to very young children focus on basic tasks like pattern recognition, counting, and basic motor skills. The average IQ for children in this age group can vary widely due to the rapid development of cognitive skills. Typical IQ scores range from 80 to 130.
- Ages 5-7: By this age, children begin to demonstrate more structured problem-solving abilities and logical reasoning. Average scores are more stable, ranging from 90 to 110.
- Ages 8-12: IQ tests become more focused on academic and verbal skills. Cognitive abilities have developed significantly, and average IQ scores typically fall within the 85-115 range.
2. IQ Scores for Adolescents (13-19 years)
As adolescents mature, cognitive abilities like abstract thinking and reasoning improve. By this stage, most individuals will have settled into a stable IQ range that can remain consistent throughout adulthood. The average IQ score for adolescents is generally between 90 and 110.
3. IQ Scores for Adults (20-64 years)
For adults, IQ scores typically remain stable, with most adults scoring between 85 and 115. As adults reach middle age, their IQ scores often reflect their experience and continued development in areas such as problem-solving and abstract thinking.
4. IQ Scores for Seniors (65+ years)
In older adults, there can be a slight decline in IQ scores as cognitive processing speed decreases. However, many seniors compensate with wisdom, experience, and verbal reasoning, keeping their scores within the average range. The average IQ for seniors usually remains between 85 and 105, depending on factors such as health and lifestyle.
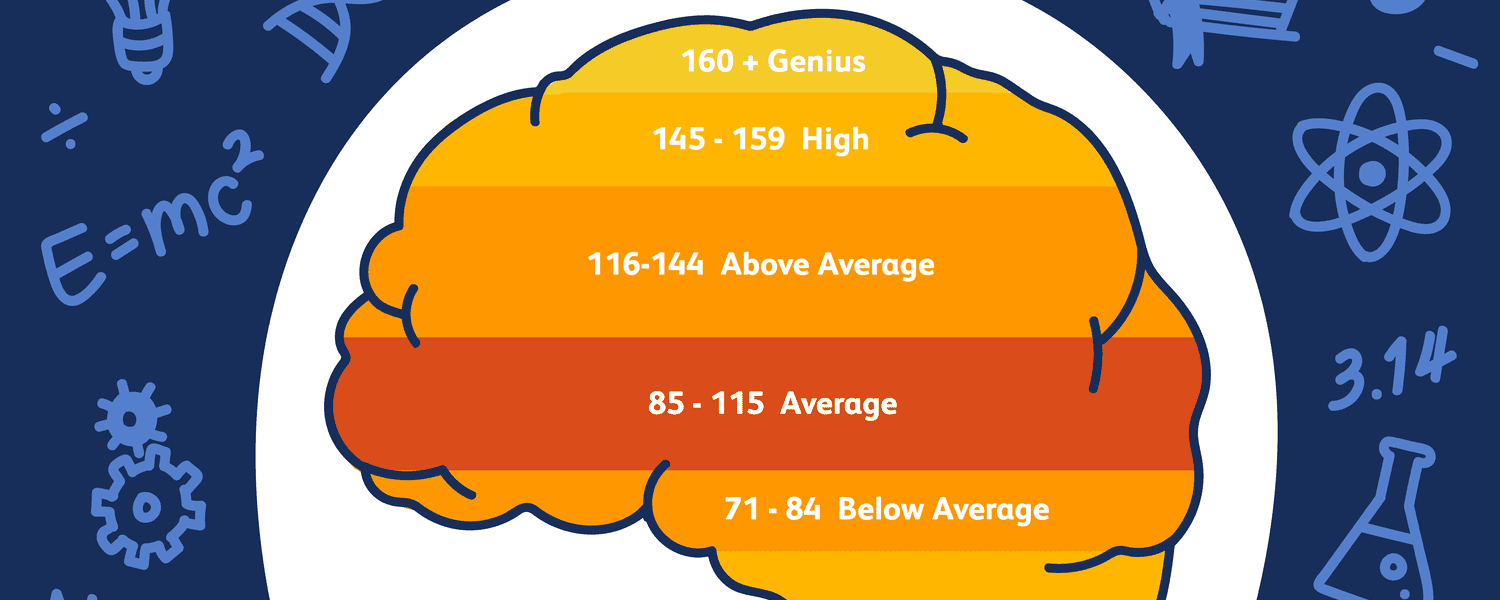
Interpreting IQ Scores
1. Below 70 (Significantly Below Average)
An IQ score below 70 is often associated with developmental delays or intellectual disabilities. Individuals in this range may require additional support in learning and day-to-day activities.
2. 70-85 (Below Average)
A score within this range indicates below-average intelligence. People may face challenges with academic tasks but can often lead independent lives with some assistance.
3. 85-115 (Average)
This range represents the majority of the population. Individuals with IQ scores between 85 and 115 are considered to have average intelligence.
4. 115-130 (Above Average)
Scores in this range reflect above-average intelligence. Individuals may excel in academic or professional settings.
5. 130 and Above (Gifted and Genius Levels)
An IQ score of 130 or higher is often associated with giftedness or genius-level intelligence. These individuals tend to excel in complex problem-solving and creative tasks.
Factors that Affect IQ Scores
1. Genetics
Research suggests that genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual’s IQ. However, environmental factors can also have a considerable impact.
2. Education and Environment
Access to quality education, stimulation during early childhood, and a nurturing environment all contribute to cognitive development, which can influence IQ scores.
3. Health and Nutrition
Good health and proper nutrition are essential for brain development, especially in children. Malnutrition, chronic illness, or exposure to toxins can negatively affect cognitive abilities.
4. Test Conditions
Conditions under which the IQ test is administered, such as the individual’s emotional state, the testing environment, or fatigue, can also affect results.